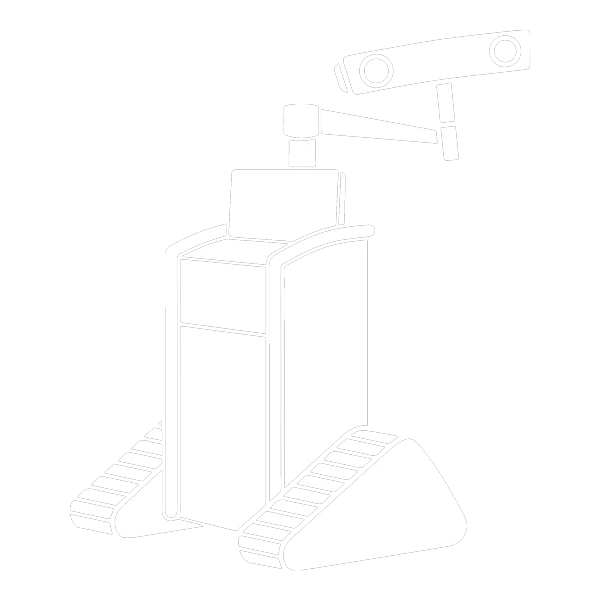
The RJB ™
RJB™ Overview
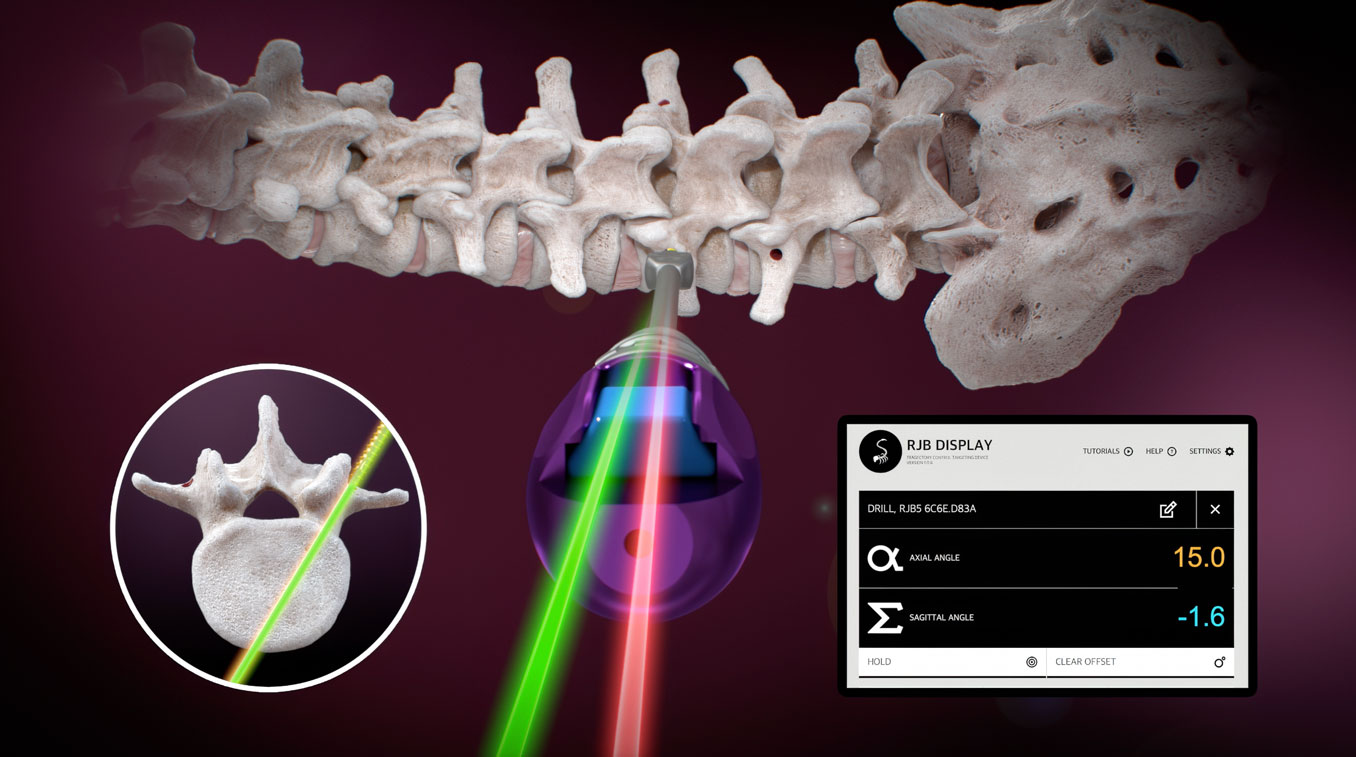
The RJB system is an Intraoperative Surgical Angle Measurement tool targeted for improving ease, efficiency and cost-effectiveness in procedures for lumbosacral pedicle screw placements.
Device Description
The RJB device can measure the axial and sagittal angles of the instrument relative to gravity. The RJB system only provides measurements for angles in two planes relative to the vertical gravitational plumb line. As such, the RJB device does not provide surgical assistance, guidance, or navigation against patient anatomy. The RJB device is not intended to replace a surgeon’s clinical judgment and has not undergone clinical evaluation. No clinical benefit has been demonstrated or is claimed. For more information, please visit the complete RJB IFU Page.
FDA Status
Ruthless Spine’s RJB device targeted for lumbosacral pedicle screw procedures is officially cleared for marketing by the FDA.
Features of the RJB™
Cost-Effective
- No need for expensive, bulky machinery.
- Pairs with Android tablets with OS 10 and above or iOS tablets with iOS 14 and above with our reliable RJB system. See IFU for further minimum tablet requirements.
Efficient
- Real-time visualization of the axial and sagittal trajectory of the instrument shaft.
- Each single-use RJB module can provide an impressive 8 hours of continuous use.
- Seamlessly attachable bluetooth-connected module.
Ease of Use
- Requires relatively little training.
- Requires no dedicated staff.
- Simple 30-second set up.
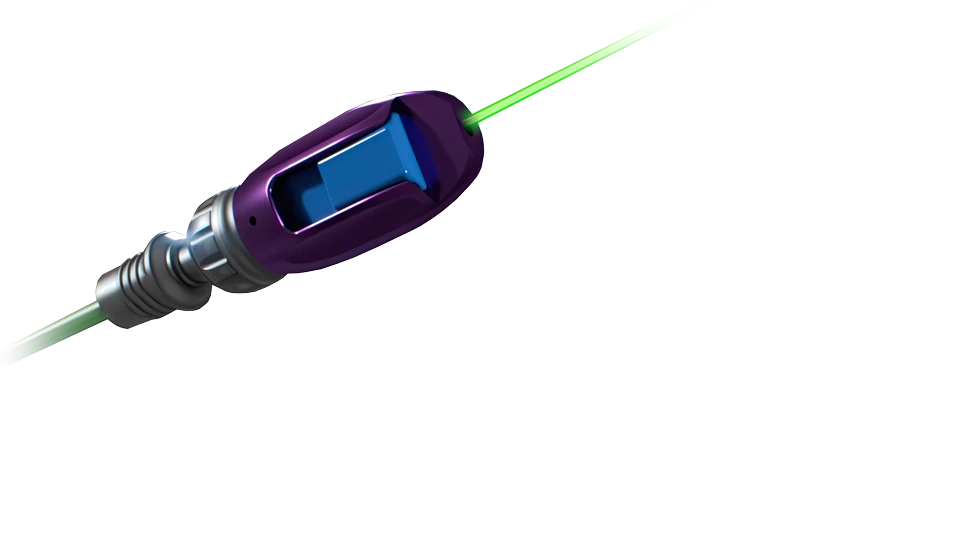


RJB™ System Components
For more information on the system components please visit the complete RJB™ IFU.
Individual Components
Part #
Description
Visual
RJB6
RJB Device

RJB-HND1
Quick Connect Axial Ratcheting Handle

RJB-PRB1
Straight Probe

RJB-PRB2
Duckbill Probe

N/A
RJB Application

Package
Components Include
Zen Pak
2 RJB Units, 1 Straight Probe, 1 Duckbill Probe, 2 Ratchets
Unit Pak
3 RJB Units, 1 Straight Probe, 1 Duckbill Probe, 2 Ratchets
Full Pak
4 RJB Units, 1 Straight Probe, 1 Duckbill Probe, 2 Ratchets

RJB™ Resources

RJB™ User Guide
Detailed User instructions on using the RJB Intraoperative Surgical Angle Measurement tool for lumbosacral pedicle screw placement.

Ruthless Spine Axial Angle Recorder
Our Axial Angle Recorder is a tool that may help surgeons record axial angles at various levels of the lumbar spine while using the RJB.
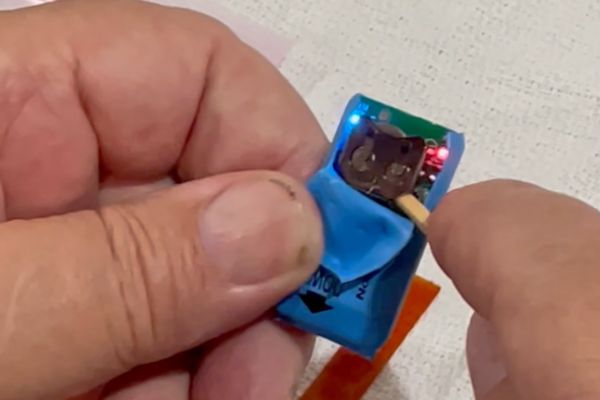

How to Change the Batteries in a RJB Demo Unit: A Step-by-Step Guide
In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through the process of safely changing the batteries in your RJB Demo unit.
Troubleshooting & Support
If you encounter any issues or have questions, please reach out for assistance. We are here to help ensure your experience with the RJB system is smooth and efficient. Contact us for troubleshooting support or inquiries.
Feel free to utilize our resources, including our complete RJB IFU, instructional videos and downloadable sheets, to enhance your understanding and use of the RJB system effectively.
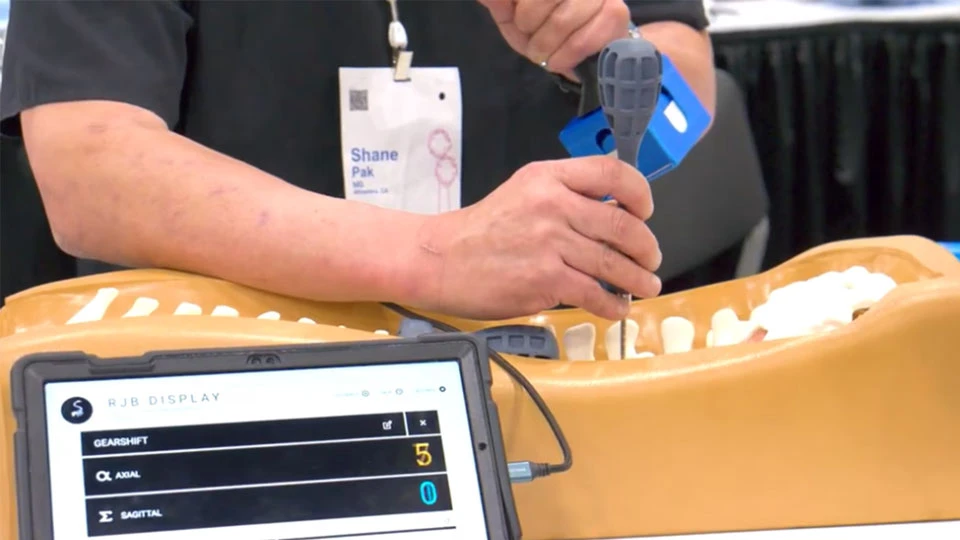

RJB™ News
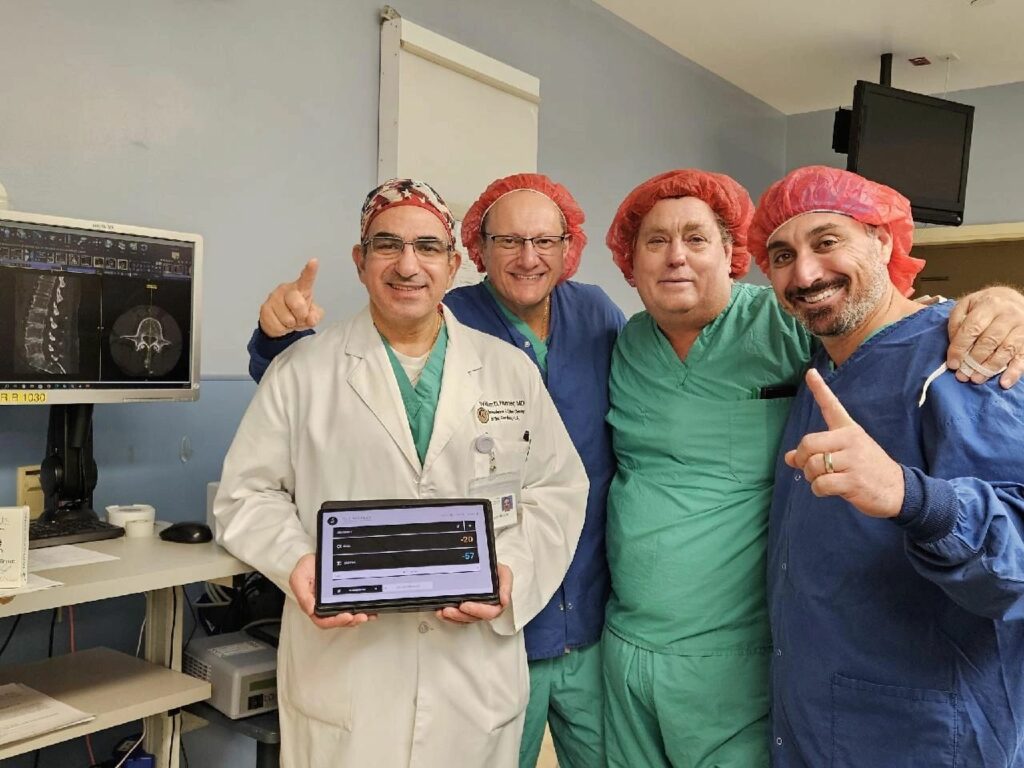

Ruthless Spine’s RJB System Hits the Market Running
Ruthless Spine proudly announces the launch of the RJB system, backed by impressive sales figures that are set to pave the way for an optimistic debt-free future.
RJB Surgical Angle Measurement tool: Impact in Africa
Learn how a group of neurosurgery residents, armed with the RJB, embarked on a mission to Liberia, Africa, to transform the landscape of spine surgery in a region with limited surgical resources.
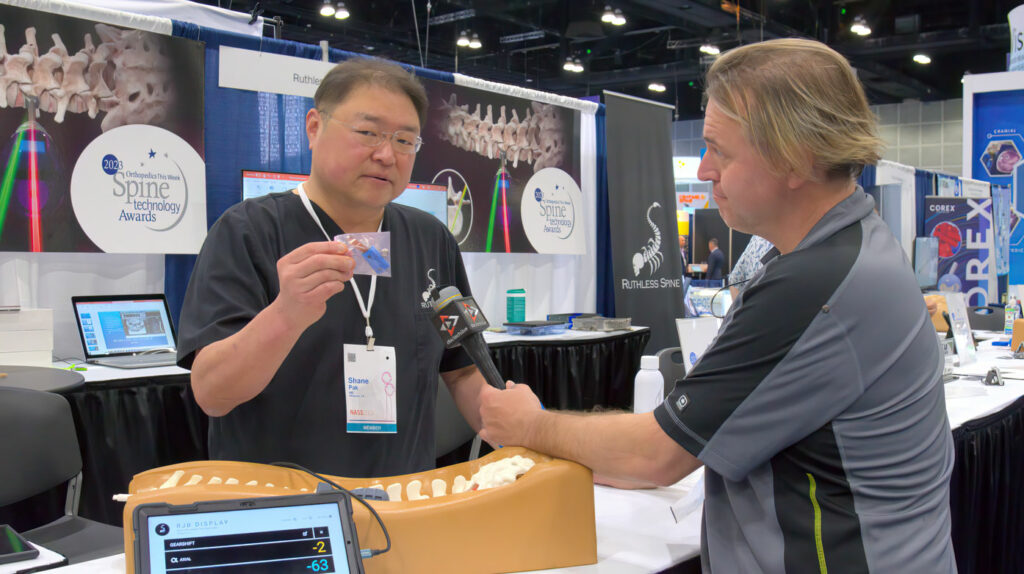

Ruthless Spine RJB At NASS 2023
The Interview With Dr. Shane Pak From Ruthless Spine At NASS 2023 Highlighted The Immense Potential Of The RJB System In Revolutionizing Spine Surgery.